Star Topology Characteristics
You can always use it to draw the physical and logical network topology diagrams for wired and wireless computer communication networks, including the extended star and the distributed star. Extended star is a type of network topology, where a network, based upon the physical star topology, has one or more repeaters between the central node which also can be called the “hub” of the “star”. Matlab 32 bit free download.
Extended Star Topology Logical Characteristics
Are capable of routing based on layer 3 addressing or additional logical levels. The term switch is often used loosely to include devices such as routers and bridges, as well as devices that may distribute traffic based on load or based on application content (e.g., a Web identifier). A typical home or small office router showing the telephone line and network cable connections A is an device that forwards between networks by processing the routing information included in the packet or datagram (Internet protocol information from layer 3). Easy data recovery with crack free download. The routing information is often processed in conjunction with the routing table (or forwarding table). A router uses its routing table to determine where to forward packets. A destination in a routing table can include a 'null' interface, also known as the 'black hole' interface because data can go into it, however, no further processing is done for said data, i.e.
Star Network Topology Logical Characteristics
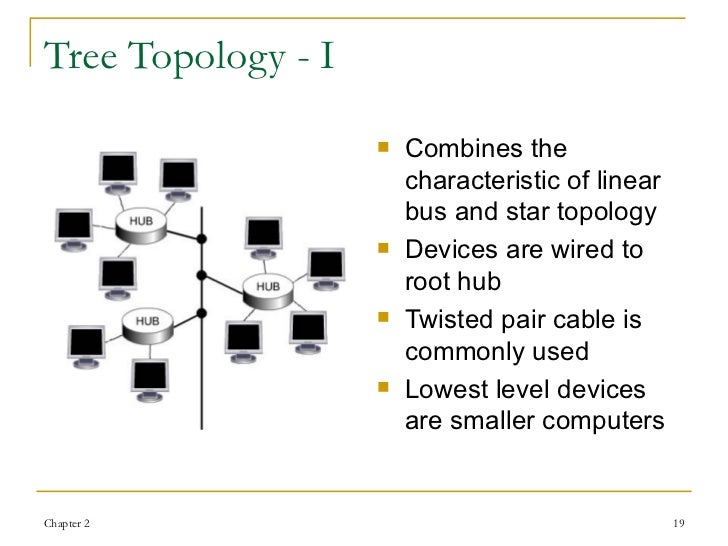
Characteristics of network topologies. Bus topology. Star topology. Each computer is connected to a central server which directs all the traffic. Network Protocol is a set of rules that governs the communications between computers on a network. What is a Network Protocol. Rules of Network Protocol include guidelines that regulate the following characteristics of a network: access method, allowed physical topologies, types of cabling, and speed of data transfer. Types of Network Protocols.
If the data is not destined for the client, the client simply discards the packet. Today’s networks use switches instead of hubs. Here’s an example of how a switch works. When client A sends data to client D, the information first travels from client A to the switch and then the switch forwards the information only to the port that client D resides on. The information does not get sent to all the clients connected to the switch, like what a hub does. This data path offers performance benefits and also security benefits. One of the major benefits of using a star topology is that if a cable breaks, it doesn’t take down the entire network like it would with a bus topology; only the workstation connected to the broken cable is affected.
The value of a permanent point-to-point network is unimpeded communications between the two endpoints. The value of an on-demand point-to-point connection is proportional to the number of potential pairs of subscribers and has been expressed as. Main article: In local area networks where bus topology is used, each node is connected to a single cable, by the help of interface connectors. This central cable is the backbone of the network and is known as the bus (thus the name). A signal from the source travels in both directions to all machines connected on the bus cable until it finds the intended recipient.
A star network usually uses twisted pair cabling, although fiber optic can also be wired in a star configuration. Advantages and disadvantages of the star bus The star bus is one of the most popular LAN technologies, and with good reason. The table below lists some of the advantages and disadvantages of the star bus. Advantages of star bus Disadvantages of star bus • Fault tolerant • Inexpensive, flexible, and easy-to-use cable or media type • Easy to troubleshoot by removing computers from the hub or adding 'smart' hubs to diagnose problem for you • Simple to add more computers to network • Fast processing capability--up to 1000Mbps (1Gbps) • Active topology set-up (with hub as a multi-station repeater) that amplifies signal • Expensive because of additional cable and the purchase of a hub How computers communicate on a star bus When a computer on a typical star bus sends a message, it travels to the hub. If the hub is an active hub, it regenerates the signal and then sends it out via all ports to the rest of the computers on the network.